GERMANY

Germany’s academic scene is bustling, drawing in a remarkable 458,210 international students in the 2022/2023 academic year. If you’re one of these eager students looking to study in Germany, you’ll likely need to go through the student visa process with your local German embassy or consulate.
In Germany, visa and residence permit requirements depend on your nationality. Some students skip both, some only need a residence permit, while most require both a visa and a residence permit.
Quick Summary
- If your studies last up to 90 days, a Schengen visa is needed, though some countries have exemptions. For studies exceeding 90 days, a national visa and potentially a residence permit are required, but exceptions apply for specific nationalities.
- The main steps to apply for a Germany student visa are:
- Locate the nearest German embassy.
- Review country-specific requirements.
- Schedule a visa appointment.
- Prepare and check your documents.
- Pay the processing fee.
- Prepare for the interview.
You can get a German student visa for various activities, including language courses, preparatory programs, internships, and university degree studies.
Types of Germany Study Visas
As we have already established, two types of visas allow you to study in Germany: the Schengen visa (C visa) for short courses lasting up to three months, and the national visa (D visa) for courses lasting more than three months.

The national German visa for studies can be issued for a range of study levels and degrees. This includes undergraduate, exchange, graduate, or postgraduate studies. This also covers participation in a pre-academic measure or a non-academic German language course.
There are three types of German national visa (D visa) issued to students that you can apply for depending on your circumstances:
- German Student Visa. If you have been admitted to a German higher education institution and are ready to start your studies in a higher education program.
- German Student Applicant Visa. If you have applied to a state-approved higher education institution/state-approved provider of preparatory courses and have a good chance of getting admitted, but do not yet have a certificate of admission or confirmation of application.
- German Language Course Visa. If you want to attend intensive German language courses in Germany without pursuing university studies.
What Are German Student Visa Requirements?
The most important requirements to apply for the German Student Visa are:
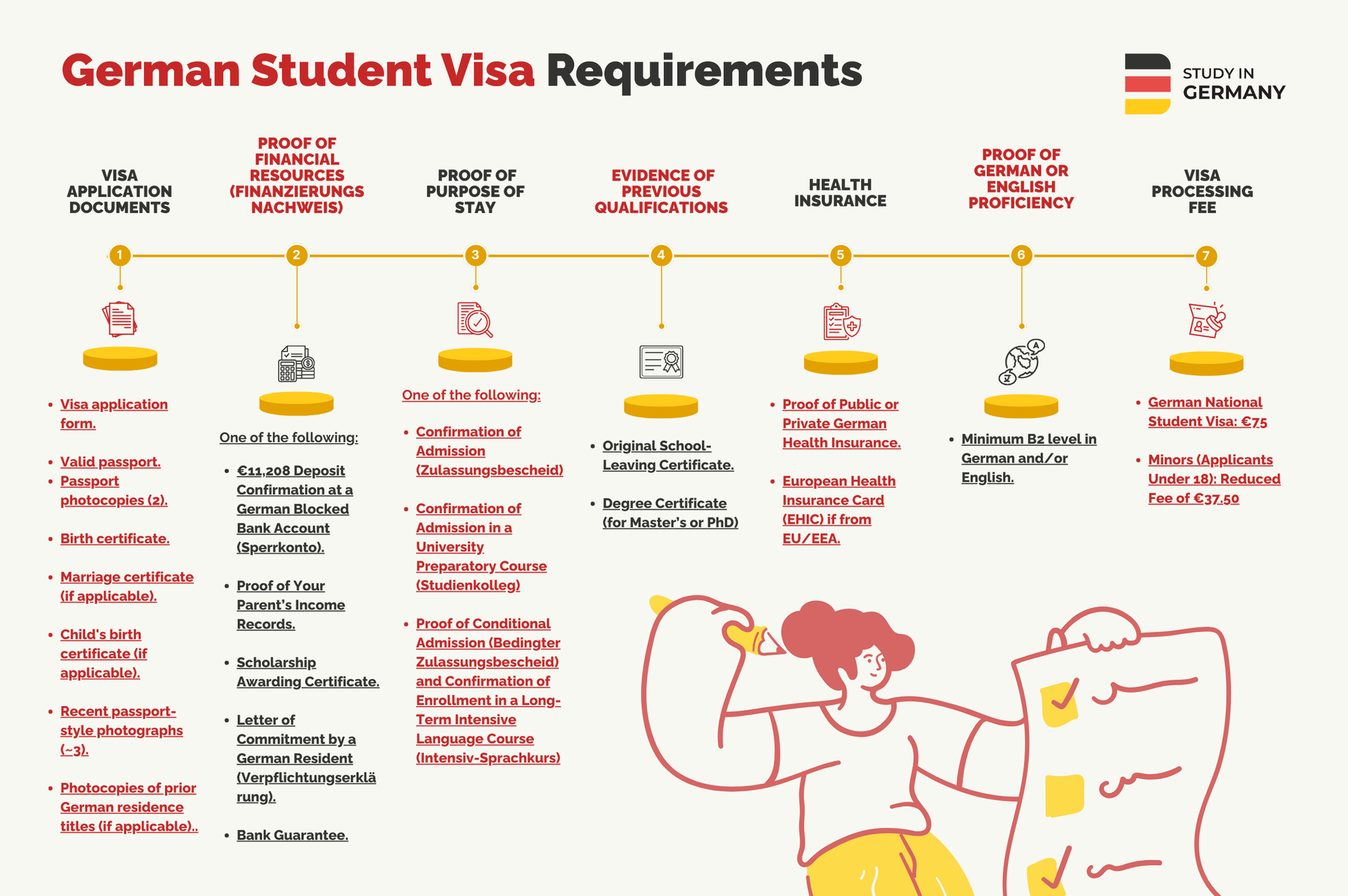
1. Visa Application Documents
- Duly filled out and signed national visa application form.
- Valid passport.
- Two photocopies of your passport.
- Birth certificate.
- Marriage certificate (if applicable).
- Your child’s birth certificate (if applicable).
- Recent passport-style photographs (up to 3).
- Photocopies of previous German residence titles (if applicable).
2. Proof of Financial Resources (Finanzierungsnachweis)
You can submit one of the following to prove your financial resources:
- €11,904 deposit confirmation at a German blocked bank account (Sperrkonto).
- Sufficient proof of your parent’s income records and financial assets.
- Scholarship awarding certificate specifying coverage amount.
- Letter of commitment by a German resident (Verpflichtungserklärung) who can cover your expenses during your studies.
- Bank guarantee issued to you by a recognized bank.
3. Proof of Purpose of Stay
You can send any of the following:
- Confirmation of admission (Zulassungsbescheid) – issued from a recognized German educational institution, indicating your program start date and language of instruction.
- Confirmation of admission in a university preparatory course (Studienkolleg) – it can be a letter from uni-assist, confirmation of admission as an applicant, communication with the university regarding conditions for final admission, or proof of having been confirmed as a participant in the course.
- Proof of conditional admission (Bedingter Zulassungsbescheid) and confirmation of enrollment in a long-term intensive language course (Intensiv-Sprachkurs) lasting over 6 months with a minimum of 18 weekly hours – it can be proof of conditional university admission (letter from uni-assist, confirmation of admission as an applicant, communication with the university regarding conditions for final admission), or proof of payment for the first three months of the course with a confirmed spot.
4. Evidence of Previous Qualifications
Submit official documents and notarized copies of the academic qualifications that apply to you. Include your original school-leaving certificate and, if applicable, your degree certificate for Master’s or PhD studies.
5. Health Insurance
Health insurance is mandatory for studying in Germany. If you’re from an EU/EEA country or have an agreement with Germany, you may use your existing insurance with a European Health Insurance Card (EHIC) or other form of health insurance. Otherwise, you must get German health insurance for your student visa and enrollment.
Many providers offer digital registration before arriving in Germany, with final details to be submitted upon arrival.
6. Proof of German or English Proficiency
To obtain a national student visa in Germany, you must prove your proficiency in the language of instruction for your chosen study program. Typically, a minimum B2 level in German and/or English is required for student visas, which can be demonstrated through language exams.
7. Visa Processing Fee (€75)
The visa processing fee for a German national student visa is €75, and minors (applicants under 18) pay a reduced fee of €37.50. You should bring this exact cash amount in the local currency when you submit your application. Some recipients of scholarships issued by a public institution may be exempt from this fee, so check with your local German embassy or consulate for specific details. There are no refunds if your visa is denied.
What Is the Required Bank Balance for a German Study Visa?
As of 2024, you must have a minimum of €11,904 in your blocked bank account when applying for a German student visa. Be aware that you can withdraw a maximum of €992 monthly from your blocked account.
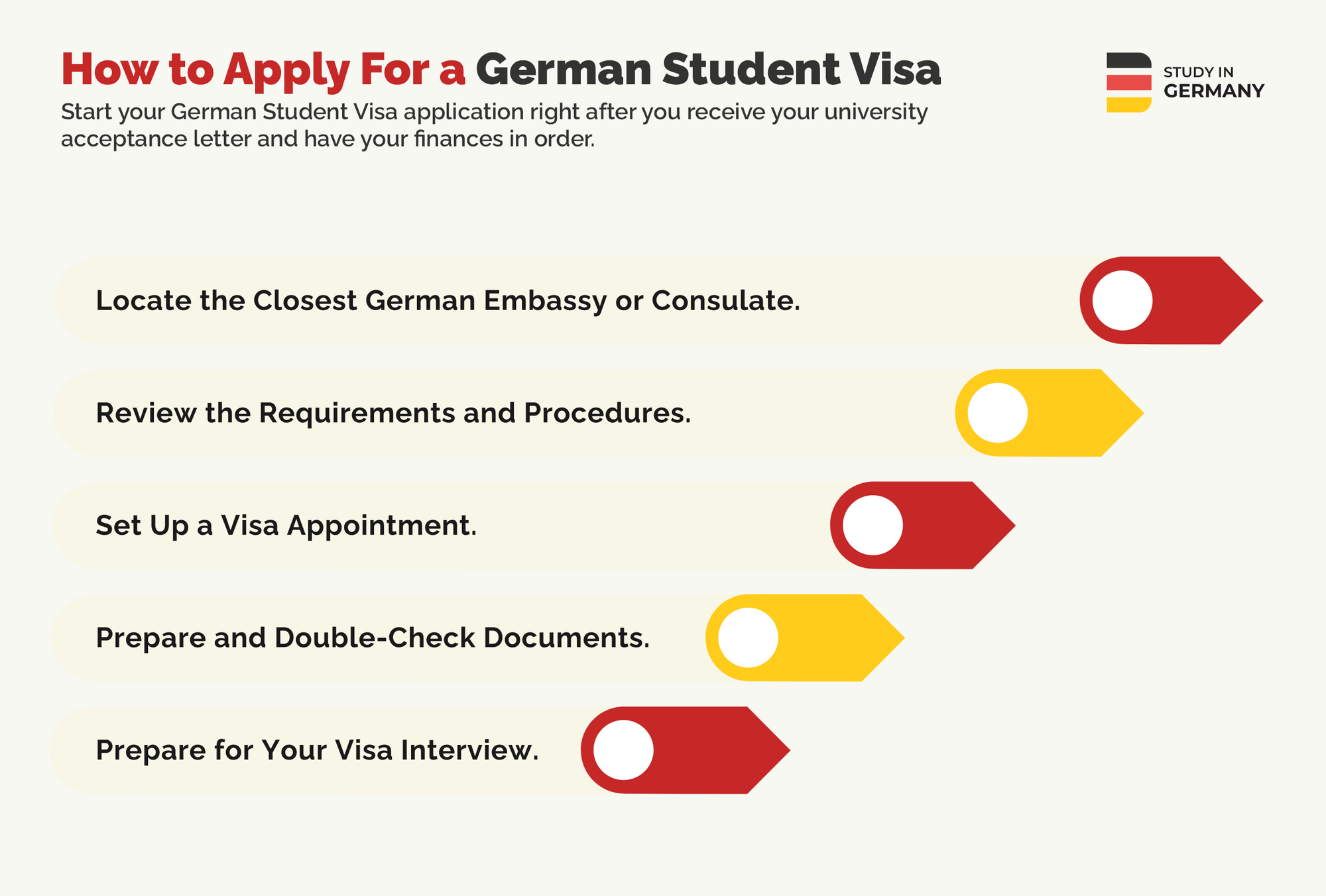
How to Apply For A German Student Visa
Once you make sure you fulfill all requirements, you can begin the German Student Visa application process. The steps you need to go through vary depending on your country, but here’s a general overview of what you’ll need to do:
- Locate the closest German embassy or consulate. You can use Google to search for an embassy or consulate in your country or a nearby country to gather more details about visa requirements and scheduling a visa appointment. All official German missions in different countries have an official website with their physical address and contact information available online.
- Review the requirements and procedures. Visit the German embassy website and navigate to the student visa section to examine your country’s specific requirements and appointment procedures. Make sure you carefully review all the information provided (especially the documents you need to have) before you set up a visa appointment.
- Set up a visa appointment. Once prepared, schedule a visa appointment through your country’s German embassy website. Some embassies may have a high volume of applications, so applying a few weeks in advance is advisable.
- Prepare and double-check documents. Once your visa appointment date is confirmed, you should double-check all of your documents to ensure everything is in order. If you follow all instructions, you can do this yourself without needing to pay any outside consultants or agencies to apply for you.
- Prepare for your visa interview. Before your visa interview, pay the non-refundable visa processing fee (€75, €35.50 for minors) and keep the payment confirmation. Prepare for the interview in advance by reviewing common student visa questions. After the interview, you’ll need to wait for the official decision on your visa status.
When To Apply For a German Student Visa
It’s a good idea to start your German Student Visa application right after you receive your university acceptance letter and have your finances in order. Many people who have been through this process suggest that applying about three months before your intended start date for your studies works well.
Important Tip: To Maximize Your Chances of Getting Your German Student Visa You Should Use a Blocked Account as Proof of Financial Resources.
A blocked account is a special type of bank account, to prove you have enough funds to live in Germany for one year.
As of 2024, as a foreigner in Germany you need a minimum of €992 euros per month for living expenses. So, you are required to have a total of €11,904 in your bank account before you apply for a German internship visa.
Germany Student Visa Processing Time
On average, it takes up to 25 days for your German student visa application to be processed. The processing time varies depending on the country and the German embassy you apply to. All other German visa applications for studies are normally processed within 3 months.
How To Get a Student Residence Permit in Germany
A student residence permit in Germany is essential for anyone who plans to study in the country for longer than 90 days and is not an EU/EEA citizen. It allows you to live and study in Germany, and you can work for a limited number of hours per year.
Here are the steps to getting a student residence permit in Germany:
Find Your Permanent Accommodation
During your first two weeks in Germany with a study visa, you should arrange for long-term accommodation if you haven’t already done so.
Register at the Local Resident’s Office
After securing long-term housing, register at the local Resident’s Office (Anmeldung). This is a mandatory step for those staying over three months, where you will get an address registration certificate (Anmeldebestätigung).
Documents needed for registration in Germany as an international student include:
- Valid passport or national ID (with a valid visa if applicable)
- Rental contract
- A confirmation letter from your landlord specifying your address
Enroll in Your Chosen Academic Program
To begin your studies, you must officially enroll at the university during the specified enrollment period mentioned in your admission letter. This process, known as matriculation, involves submitting necessary documents to the student affairs office (Studentensekretariat) at your university. You’ll also need to pay the semester fee before receiving your student ID, password, and your student ID card.
Here’s a list of the documents you’ll need to enroll as an international student in Germany:
- Application for enrollment (online or printed)
- National passport/national ID card with a valid visa (if applicable)
- Letter of acceptance from your university
- Proof of statutory health insurance in Germany
- German University Entrance Qualification or equivalent recognized qualification
Note: Your university’s International Office (Akademisches Auslandsamt) can offer the most up-to-date information for both academic and residence-related inquiries.
Apply for a Residence Permit for Studies
You will have to apply for a residence permit for students before your visa expires (if applicable). To do so, you will have to make an appointment at the local Foreigner’s Office (Ausländerbehörde) and start preparing your application documents.
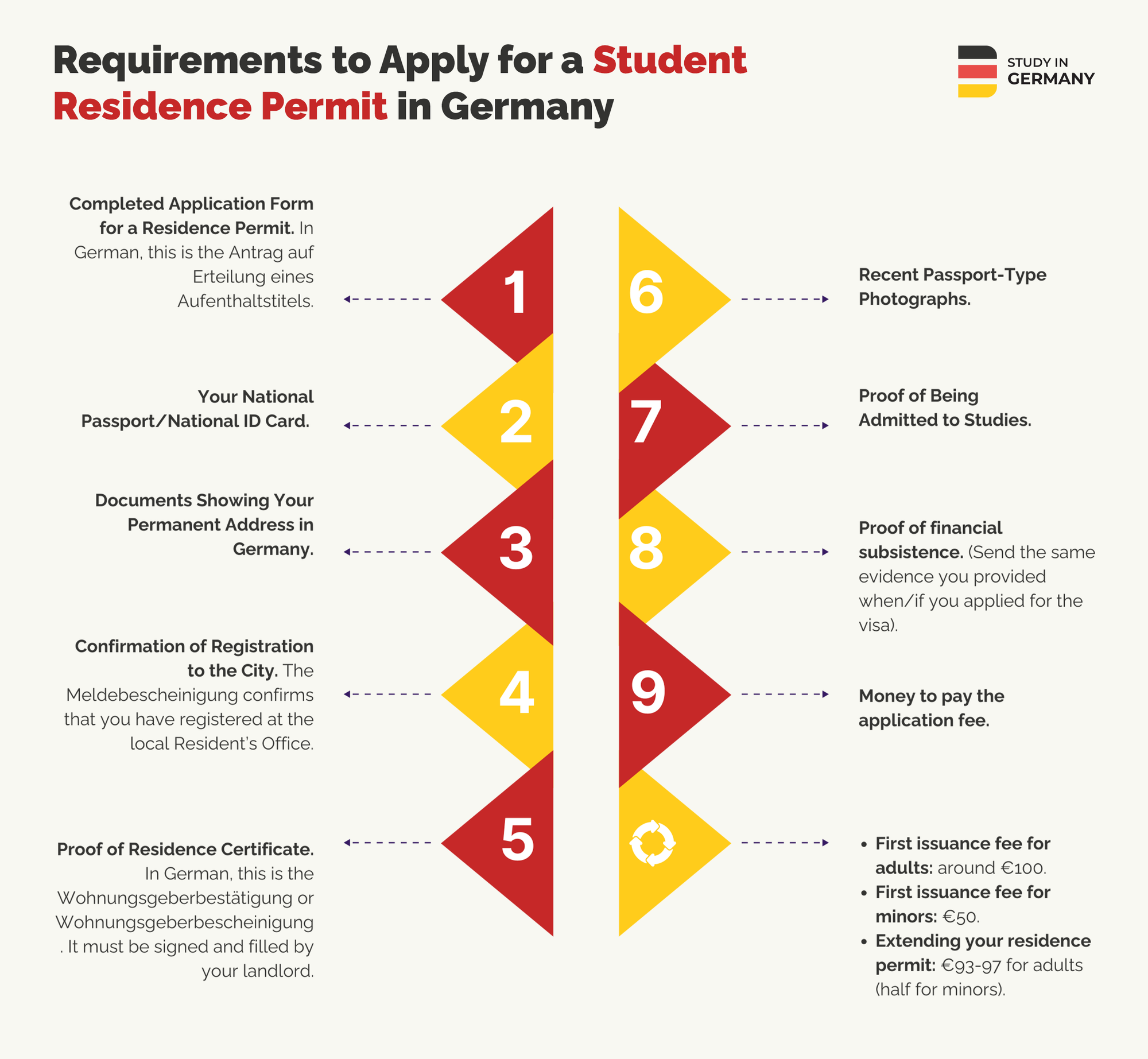
Requirements to Apply for a Student Residence Permit in Germany
To apply for a residence permit, you will need to provide the documents above:
- Duly completed application form for a residence permit. In German, this is the Antrag auf Erteilung eines Aufenthaltstitels.
- Your national passport/national ID card. It has to show you have a valid entry visa if you’ve entered with a visa.
- Documents showing your permanent address in Germany.
- Confirmation of registration to the city. The Meldebescheinigung confirms that you have registered at the local Resident’s Office.
- Proof of residence certificate. In German, this is the Wohnungsgeberbestätigung or Wohnungsgeberbescheinigung. It must be signed and filled by your landlord.
- Recent passport-type photographs.
- Proof of being admitted to studies. (e.g. certificate of enrollment, confirmation of admission, or evidence of conditional admission in studies.)
- Proof of financial subsistence. (Send the same evidence you provided when/if you applied for the visa).
- Money to pay the application fee. You’ll need to cover the application fee for a German residence permit, with costs varying by location and circumstances. For adults, the first issuance fee is around 100 euros, while it’s 50 euros for minors. Extending your residence permit usually costs 93-97 euros for adults and half that for minors.
German Student Visa FAQ
Here are some frequently asked questions (FAQ) about German student visas.
What Activities Can I Get a German Student Visa For?
You can get a German student visa for the following activities:
- Non-academic language course studies. A course lasting 3-12 months, with at least 18 hours of lessons in a week. The course must not be aimed to prepare you for further academic studies.
- Pre-academic measures. A course lasting more than 3 months, aimed to prepare you for full-time academic studies.
- Pre-academic German language courses. Participation in a preparatory course before sitting any of these recognized tests before studies must be a university prerequisite before your final admission to studies.
- Preparatory foundation course (Studienkolleg). The course has to prepare you for the qualification test Feststellungsprüfung. By passing this test, you can expect to obtain a recognized university entrance qualification (Hochschulzugangsberechtigung). (This applies if your foreign high school leaving certificate is not recognized in Germany).
- Propaedeutic course studies (Propädeutikum). These courses must offer language and academic skills and specific knowledge regarding Germany’s education system and methodology. They must be held by the education provider you’ll be studying at.
- Partaking in a mandatory preliminary internship. Participation in an internship must be a precondition for admission to the study program, i.e. at a University of Applied Sciences.
- University degree awarding studies. You must have received the confirmation for admission to studies from a recognized higher education provider here. This is relevant for studies leading to a recognized higher education degree, such as bachelor’s (BA, BSc, BSEng), master’s (MA, MSc, MEng), or PhD.
What Is a University Admission Confirmation Letter?
A university admission confirmation letter is a written document that confirms your acceptance as a student. This letter typically includes the following information:
- Details of the educational institution where you have been admitted for study.
- An acceptance reply card, which requires your confirmation of acceptance for the offered place by replying to the university admission office with a signed card.
- Enrollment deadline, indicating the dates by which you should register as a student.
- Exam dates, specifying when the German language test or university preparatory entrance examination will be held (if you have been conditionally admitted).
- Information about the orientation day, an event where new students are informed about the university’s facilities and activities.
What Is a Conditional Admission Confirmation Letter?
A conditional admission is a decision from the university’s admission office that comes after your application. It means you have to meet extra requirements before you can officially become a student at that university.
These requirements may involve participating in preparatory measures and/or passing specific pre-academic tests.
What Is the University Entrance Qualification (HZB)?
The University Entrance Qualification (HZB) is a certificate that allows you to study at a German university. It can be your school leaving certificate or a combination of other qualifications, depending on your home country.
This certificate is essential for applying to German universities as it confirms the equivalence of your foreign education to the German Abitur, which is required for enrollment.
If your previous education doesn’t meet HZB requirements, you may need to complete a preparatory course (Studienkolleg) to qualify for university study in Germany.
Which Language Certificates Are Accepted for Studying in Germany?
When planning to study in a German-taught program, each university sets its own language requirements, and specific programs may have different standards.
In most cases, German universities commonly accept these certificates and levels as proof of language proficiency:
- DSH (Deutsche Sprachprüfung für den Hochschulzugang) – DSH 2
- TestDaF (Test of German as a Foreign Language) – TDN 4
- Certificates issued by the Goethe-Institut – C1 or C2
- The DSD German language diploma (Deutsches Sprachdiplom der Kultusministerkonferenz) – DSD II
Similarly, with English-taught programs, each university and program will have its own requirements.
To demonstrate English proficiency for programs taught in English, universities in Germany commonly accept these certificates and scores:
- IELTS (International English Language Testing System) – 6.0, 6.5, 7.0
- TOEFL (iBT or PBT- iBT 94-72, PBT 626-543
- Evidence of English being the language of instruction in previous studies – B2-C2
- Cambridge English language certificates (FCE, CAE, CPE)
- TOEIC or UNIcert are often accepted
What Does “Transcripts of Grades From Earlier Studies” Refer To?
Transcripts of grades from earlier studies are official documents that provide a detailed record of your academic performance and the grades you received in your previous educational courses or programs. These transcripts typically include information such as the names of the courses, the grades or marks obtained, the credit hours or units, and the dates of completion.
What is an Accreditation Certificate?
An accreditation certificate is a document issued by the Ministry of Education or a similar authority in your country, recognizing an education provider or study program. This certificate confirms that your qualification is granted by a state-approved institution.
What Is the APS Certificate?
The APS Certificate, issued by the Academic Evaluation Center (Akademische Prüfstelle – APS), is an official document from the German Embassy and DAAD. It verifies the authenticity of educational backgrounds and certificates for students from China, Vietnam, and India.
This certificate is mandatory if you’re applying to German universities from these regions, confirming that your qualifications meet German standards.
What Does “Notarized Documents” Mean?
“Notarized documents” refer to official copies of documents that have been certified or authenticated by a notary public or a similar authorized legal official. These copies are often required to ensure the validity and accuracy of the submitted documents during the application process for a German university.
What Does the Equivalent of a Bachelor’s/Master’s Degree in Germany Mean?
The equivalent of a bachelor’s or master’s degree in Germany refers to the recognition and acknowledgment of foreign academic qualifications as being on par with the corresponding German degrees.
This means that if your degree from another country is considered equivalent, it holds the same academic value and level of qualification as a bachelor’s or master’s degree awarded by a German university.
The Central Office for Foreign Education (ZAB) evaluates foreign qualifications, and you can check their database (anabin) to see if your degree is recognized in Germany.
What’s a Curriculum for Studying in Germany?
The curriculum for studying in Germany is a document that demonstrates your academic background and how it aligns with the requirements of the specific university program you wish to pursue in Germany. It lists the understanding and skills acquired in previous studies, provided they are relevant to the university program you are applying for.
This document should be accompanied by a catalog of study modules that offers a detailed description of the degree program, department, division, and university.
What Information Should I Include in the Curriculum Vitae?
When a CV is required, you must include information about your earlier formal and informal education, internships, employment activity, and national service in chronological order.
It must also cover information about your skills and other special talents. The formal education must include information about schools and universities (if applicable) where you’ve studied, the study subject, and graduation dates.
Can I Bring My Family to Germany on a Student Visa?
You can bring your family to Germany if you have a student visa, but there are some conditions. You need to have a residence permit and be married before getting the permit. You also have to plan to stay in Germany for over a year. It’s important that you can support yourself and your family without needing public help.
Who you can bring includes your spouse, children under 16, and in some cases, older children or other family members in difficult situations. To come to Germany, your family will need to apply for a family reunification visa at the German embassy or consulate in your home country.